ManyToOne 관계를 가지고 있는 자식 엔티티를 등록할 때, 단순히 외래키만을 사용하지만 엔티티 자체를 조회해서 사용하는 모습이 더러보였다. 불필요한 리소스 낭비이기 때문에 좀 더 효율적으로 연관관계를 사용하는 게 필요해 보여 정리하게 됐다.
@ManyToOne관게는 가장 흔한 관계이기 때문에, 어떻게 적절하게 맵핑하는 지를 아는 것은 App의 성능에 큰 영향을 준다.
테이블 관계
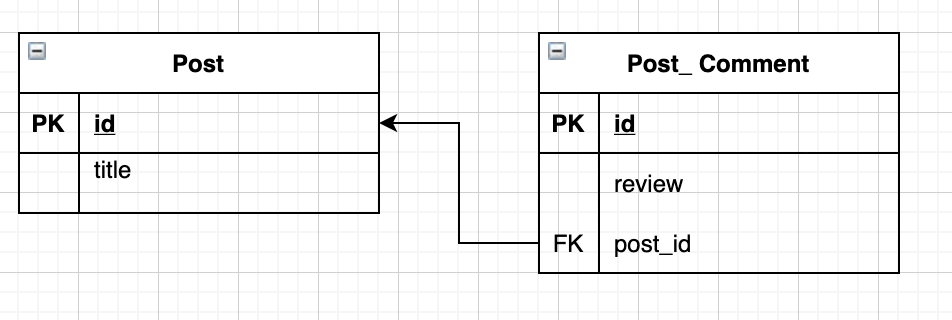
post_comment 테이블은 post테이블의 id를 외래키로 가지는 ManyToOne 관계
@Entity
@Table
public class PostComment {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String review;
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinColumn(name = "POST_ID")
private Post post;
//Getters and setters 생략
}중요한 점은 @ManyToOne 관계는 FetchType.EAGER 전략을 기본값으로 가지기 때문에, FetchType.LAZY로 변경해야 한다.
(N+1 query issue와 불필요한 fetch을 피하기 위함)
ManyToOne 관계 persist
Post entity를 persist했다고 가정
entityManager.persist(
new Post()
.setId(1L)
.setTitle("High-Performance Java Persistence")
);여기에서 자식 엔티티를 persist할 때, 부모엔티티를 fetch하기 위해서 find를 사용하는 실수를 한다.
Post post = entityManager.find(Post.class, 1L);
entityManager.persist(
new PostComment()
.setId(1L)
.setReview("Amazing book!")
.setPost(post)
);또는 Spring Data JPA를 사용할 경우, 같은 문제를 발생시키는 findById를 사용하는 경우
Post post = postRepository.findById(1L);
commentRepository.save(
new PostComment()
.setId(1L)
.setReview("Amazing book!")
.setPost(post)
);
PostComment 엔티티를 persist할 때, 위의 두 가지 메소드를 사용하면 다음과 같은 SQL이 실행된다.
SELECT
p.id AS id1_0_0_,
p.title AS title2_0_0_
FROM post p
WHERE p.id=1
INSERT INTO post_comment (
post_id,
review, id
)
VALUES (
1,
'Amazing book!',
1
)필요한 속성은 단지 외래키인 post_id이기 때문에, Post 엔티티를 fetch할 필요가 없다. 하지만 Select query가 실행된 모습을 볼 수 있다.
이러한 불필요한 실행과 목적에 적합한 사용을 하기 위해선 getReference를 사용하면 된다!!find를 사용하는 대신에, 아래처럼 Reference를 사용해보자.
Post post = entityManager.getReference(Post.class, 1L);
entityManager.persist(
new PostComment()
.setId(1L)
.setReview("Amazing book!")
.setPost(post)
);만약 SpringData JPA를 사용한다면 getOne을 사용하자.
Post post = postRepository.getOne(1L);
commentRepository.save(
new PostComment()
.setId(1L)
.setReview("Amazing book!")
.setPost(post)
);실행된 쿼리를 보면 불필요한 Select가 사라진 것을 볼 수 있다.
INSERT INTO post_comment (
post_id,
review, id
)
VALUES (
1,
'Amazing book!',
1
)ManyToOne 관계 Fetch
PostComment 엔티티를 fetch하고 @ManyToOne 관계인 Post 엔티티에 접근할 때, FetchType.LAZY 전략을 사용하고 있다고 가정해보자.
PostComment comment = entityManager.find(PostComment.class, 1L);
LOGGER.info(
"The post '{}' got the following comment '{}'",
comment.getPost().getTitle(),
comment.getReview()
);hibernate는 다음처럼 부차적인 select를 실행시킨다.
SELECT
pc.id AS id1_1_0_,
pc.post_id AS post_id3_1_0_,
pc.review AS review2_1_0_
FROM post_comment pc
WHERE pc.id = 1
SELECT
p.id AS id1_0_0_,
p.title AS title2_0_0_
FROM post p
WHERE p.id = 1
The post 'High-Performance Java Persistence' got the following comment 'Amazing book!'
이러한 부차적인 Select 쿼리를 피하기 위해선, JOIN FETCH을 사용하여 post를 fetch하면 된다.
PostComment comment = entityManager.createQuery("""
select pc
from PostComment pc
join fetch pc.post
where pc.id = :id
""", PostComment.class)
.setParameter("id", 1L)
.getSingleResult();
LOGGER.info(
"The post '{}' got the following comment '{}'",
comment.getPost().getTitle(),
comment.getReview()
);hibernate는 부모 자식 엔티티를 fetch하기 위해서 단 한번의 sql query를 실행을 한다.
SELECT
pc.id AS id1_1_0_,
p.id AS id1_0_1_,
pc.post_id AS post_id3_1_0_,
pc.review AS review2_1_0_,
p.title AS title2_0_1_
FROM post_comment pc
INNER JOIN post p ON pc.post_id = p.id
WHERE pc.id = 1
The post 'High-Performance Java Persistence' got the following comment 'Amazing book!'
또한 JOIN FETCH는 사용하면, 영속성 컨텍스트(Persistence Context)가 close되었을 때 @MantyToOne관계에 접근할 경우 발생하는 LazyInitializationException를 피할 수 있다.
'JAVA > JPA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JPA] 성능 최적화하기_N+1 문제 (0) | 2021.11.18 |
|---|---|
| [동시성] 동시성 문제 해소하기(JPA)_개념 (0) | 2021.10.10 |
| [Hibernate] @Notnull vs @ NotEmpty vs @NotBlank (0) | 2018.06.28 |
